Stein Guldbrandsoy ABB Energy Industries Bergen, Norway, stein.guldbrandsoy@no.abb.com

In 2016, global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions were 31.2 percent higher than in 1990, with an average annual increase of 0.9 percent since 2010. The sectors that contribute the largest shares of GHG emissions are energy supply (35 percent) and industry (21 percent) [1]. There is a widespread recognition that these increases cannot be stopped and reversed without significantly scaling up energy efficiency. In fact, the IEA estimates that energy efficiency could provide more than 40 percent of the emissions abatement required by 2040 to be in line with the Paris Agreement [2].
The achievement of climate goals will be also assisted by increased use of carbon capture and storage (CCS) and renewable energy. The latter is growing particularly strongly: In 2017, 17 percent of the world’s energy growth came from renewable sources – the largest increase on record – and investment in renewables is expected to reach $7.4 trillion (cumulative) by 2040 [3]. The move to broader energy ecosystems could reduce annual CO₂ emissions by 900 million tons →02.
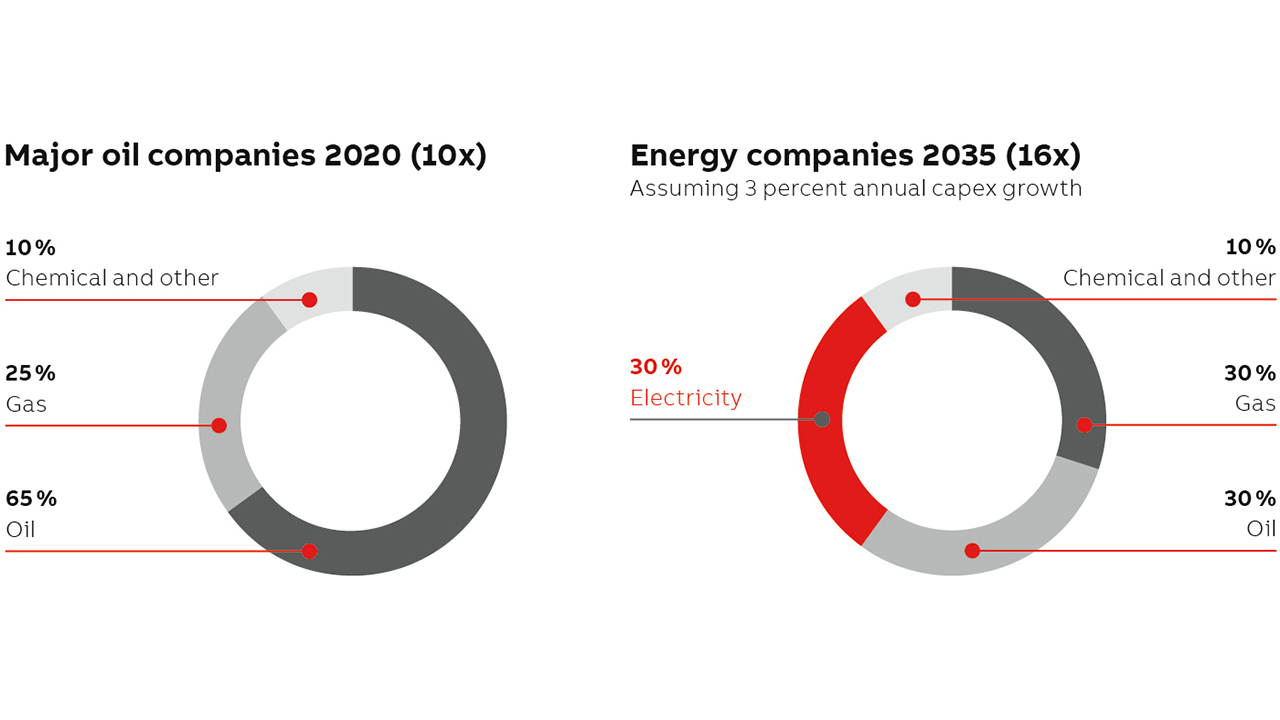
How are the energy majors reacting?
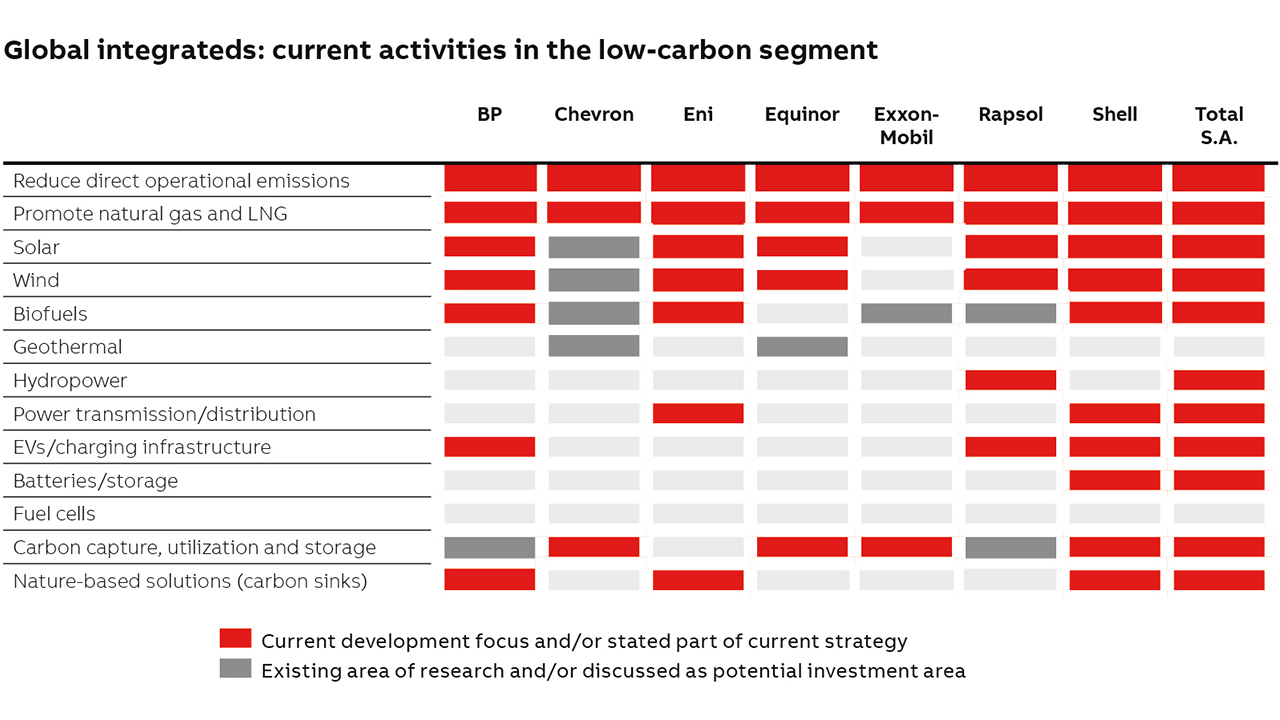
The major energy companies – including BP, Shell, Total, Chevron, Eni and Equinor – are increasingly investing in low-carbon technologies and clean-energy start-ups by nurturing companies working in areas such as CCS as well as wind and solar. However, strategy varies by IOC (an IOC is a privately owned international oil company, as opposed to an NOC, which is a national oil company) →03. Increasing cost pressures and an industry shift towards more remote and autonomous operations are also key drivers for this energy transition.
How ABB technology can help
In all the topics mentioned above – energy efficiency, CCS, low-carbon approaches and renewables – ABB technology helps customers on their energy journey so they can transition to a safer and more sustainable future. ABB’s innovative and integrated solutions digitalize, automate and electrify the oil and gas industry to improve safety, reduce carbon emissions and eliminate waste.
Automation and digitalization
Automation and digitalization are perhaps the most important methods used to support emissions reduction and increase sustainability, safety and efficiency. Here, ABB is assisting oil and gas operators to embrace low-carbon, energy-efficient production via process automation, asset management and digitalization solutions. These solutions address resource and consumption considerations, pinpoint optimal productivity levels, drive down OPEX and provide digital insights that are key drivers in helping companies to increase environmental sustainability – ie, reduce energy use and emissions →04. The Aasta Hansteen case study presented below illustrates some of these points.
Electrification
According to the World Economic Forum, electrification is critical for decarbonization [4]. Up until 2050, demand for electricity is forecast to grow seven times faster than that for other energy sources. The primary driver of this growth is the electrification of the construction, transport and industrial sectors.
To meet the electrification demands of oil and gas customers, ABB is developing new power distribution and conversion technologies and solutions.
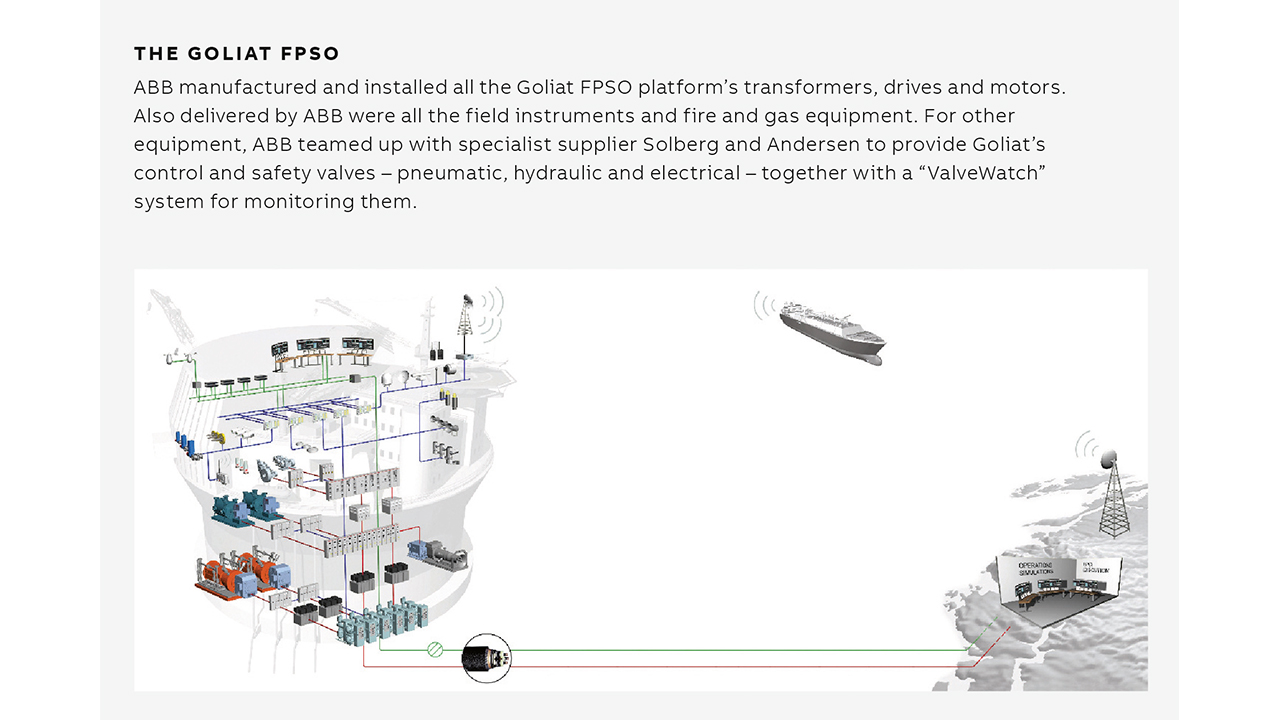
The Goliat FPSO
ABB manufactured and installed all the Goliat FPSO platform’s transformers, drives and motors. Also delivered by ABB were all the field instruments and fire and gas equipment. For other equipment, ABB teamed up with specialist supplier Solberg and Andersen to provide Goliat’s control and safety valves – pneumatic, hydraulic and electrical – together with a “ValveWatch” system for monitoring them.
Accessing new energy markets
Many companies are now looking to broaden their energy mix. ABB supports automation and digitalization of the new energy markets, including wind, solar, geothermal and zero-emission hydrogen production. Though oil and gas will be around for a long time to come, ABB’s efforts help companies focus on how to integrate more renewable energy sources into their portfolios.
Managing availability and resilience of supply through storage
ABB is actively involved with projects that harness and store energy to ensure power is always available. Core competence here includes smart control, planned management of charge/discharge cycles and the capability to island individual sites or an entire local network from the main power grid. With an effective spinning reserve, ABB can ensure energy resilience is maintained with a level of charge suitable to cover a generation or transmission outage.
ABB will provide Woodside, Australia’s largest independent oil and gas company, with a containerized, plug-and-play ABB Ability™ PowerStore™ battery storage system that is capable of remote management of operations and service. The system will be installed on the Goodwyn A platform, shown, located about 135 km northwest of Karratha in Western Australia and will replace one of the six existing gas turbine generators. A dedicated ABB Ability™ Microgrid Plus control system will act as the brain of the solution and it will also be possible to operate the microgrid remotely →05.

CCS
ABB is currently supporting the CCS pilot project at Imperial College London (ICL), where the Chemical Engineering department is leading the charge in developing a best practice for capturing and storing CO₂. ICL’s CO₂ pilot-scale absorption plant has an extensive selection of the same ABB proven products and systems that are used in a broad range of industrial applications worldwide. The plant gives students hands-on experience of the wide range of equipment ABB supplies to CCS projects – for example, Statoil’s pioneering large-scale CCS process at the Sleipner field, Equinor’s Snøhvit field in the inhospitable southern Barents Sea and Statoil's European Carbon Dioxide Technology Centre at Mongstad in Norway, which Statoil jointly owns with Shell and Gassnova. ABB automation systems monitor and control all three sites, to manage not only the complex carbon capture process but the production processes as well. At Snøhvit, for instance, ABB supported delivery of control and monitoring of the three subsea fields, the sea-to-shore multiphase pipeline, the liquified natural gas processing plant and ship loading. The company also supplied safety automation systems (SASs), incorporating a process and control data acquisition system, and an electrical control and supervisory system (ECSS). As a result, the entire development, under normal conditions, is controlled by just three or four operators in the control room. The ICL training plant is ideal for familiarizing students with the very diverse set of technical challenges found in sophisticated applications such as these.
The extent of ABB’s commitment to safety, efficiency and sustainability in the oil and gas business is best illustrated by reference to some projects that use the power of automation, digitalization and electrification to help customers operate more efficiently and with less energy intensity.
Subsea JIP for electrification – Norway
In 2013, ABB entered a five-year Subsea Joint Industry Project (JIP) with Equinor, Total and Chevron to design and deliver subsea transmission, distribution and power conversion systems for underwater pumps and gas compressors. These systems were to be used for upcoming and existing oil and gas processing fields in the Norwegian Continental Shelf (NCS), the Gulf of Mexico and several other offshore regions.
Following the completion of a 3,000-hour shallow-water test in late 2019, ABB’s pioneering subsea power distribution and conversion technology system is now commercially viable, bringing groundbreaking potential for cleaner, safer and more sustainable offshore oil and gas production.
When pumps and compressors are moved to the seabed, production of oil and gas from new and existing deepwater fields is improved and costs lowered. With subsea operations, oil and gas producers may realize about 20 to 30 percent savings on overall expenses over a 30-year operational life, as well as a 25 percent faster project execution and completion.
ABB’s complete subsea power distribution and conversion system includes a step-down transformer, medium-voltage variable-speed drives and switchgear, low-voltage power distribution, power electronics and control systems. The new subsea electrical infrastructure and equipment is controlled by ABB’s all-in-one ABB Ability™ 800xA system, which collects real-time data to use for condition monitoring and predictive analytics that optimize performance and productivity. The system gives oil and gas operators access to a reliable and safe power supply of up to 100 MW as far as 600 km offshore and at depths of 3,000 m that is designed to withstand harsh underwater conditions.
Having oil and gas processing facilities on the seabed reduces overall maintenance, with substantial cost savings. The subsea power solution could offer CAPEX savings of more than $500 million, for example, if eight consumers, such as pumps or compressors, are linked through a single cable over 200 km from other infrastructure, according to a specific field development case.
This world-first means that moving the entire oil and gas production facility to the seabed is no longer a dream. Remotely operated, increasingly autonomous, subsea facilities powered by lower carbon energy are more likely to become a reality as we transition toward a new energy future.
Operational efficiency gains with ABB Ability™ System 800xA on Aasta Hansteen – Norway
Located in 1,300 meters of water in the Norwegian Sea, about 300 kilometers west of Sandness-jøen, Aasta Hansteen is Norway’s deepest field development. It comprises two subsea templates connected to a spar platform with Norway’s first steel catenary risers →06.

Aasta Hansteen is operated by majority-partner Equinor, along with Wintershall, OMV and ConocoPhillips. It holds about 51 billion m³ of dry, low-CO₂-content recoverable gas reserves that will be transported through the Polarled pipeline to Shell’s Nyhamna onshore gas plant in Norway.
On Aasta Hansteen, ABB has installed integrated safety, automation, electrical and telecommunication systems based on ABB Ability™ System 800xA. The platform includes a condition monitoring system for over 100,000 maintenance conditions from 4,000 pieces of equipment, tools for alarm management and alarm rationalization, several safety-critical applications, and a data storage solution to store all alarms and events.
ABB’s flagship digital platform reduced manual interventions by 98 percent, saving more than a month in commissioning time. Production availability can increase, corresponding to one or two days of production as full productivity is reached faster with each start-up (production value per day is approximately $5 million).
Aasta Hansteen will strengthen the position of Equinor and the NCS as a long-term, reliable supplier of gas to Europe and the United Kingdom.
A transition to a safer and more sustainable world
The JIP and Aastad Hansteen examples described above are world-firsts but are only some of the many projects in which ABB’s innovative and integrated solutions have digitalized, automated or electrified oil and gas applications. ABB is working energetically with all customers to ensure their plants operate more efficiently and with less energy intensity to make the use of our planet’s resources safer, smarter and more sustainable by reducing carbon emissions and lowering waste.
References
[1] United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Greenhouse Gas Emissions.” Available: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions. [Accessed May 26, 2020].
[2] International Energy Authority, “Energy Efficiency 2018: Analysis and outlooks to 2040, Fuel report – October 2018.” Available: https://www.iea.org/reports/energy-efficiency-2018. [Accessed May 28, 2020].
[3] Offshore Energy, “NEO 2017: Renewables set for $7.4 trillion in new investment by 2040.” Available: https://www.offshore-energy.biz/neo-2017-renewables-set-for-7-4-trillion-in-new-investment-by-2040/. [Accessed May 26, 2020].
[4] D. Puglielli, World Economic Forum, “How electrification can supercharge the energy transition,” 25 April, 2019. Available: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/04/electrification-energy-transition-decarbonization-climate-change/. [Accessed May 28, 2020].