![ABB Corporate Research scientist Jürgen Schuderer (second from left) receives the prestigious PCIM Europe 2019 best paper award for the ABB publication ”High-Power SiC and Si Module Platform for Automotive Traction Inverter“ [1].](https://resources.news.e.abb.com/images/2019/7/5/0/PCIM_award.jpg)
The International Energy Agency’s electric vehicle outlook projects a rapid growth from three million vehicles in 2017 up to 228 million electric vehicles by 2030 [2]. This tremendous growth presents the need for cost-effective and reliable power electronic converters for use in the powertrain of passenger and commercial vehicles. Power semiconductor modules are used in the traction inverter to control motor torque and speed via pulse width modulation. The following aspects are especially important for the automotive sector:
- Costs: Generally, cost reduction is the dominant development target and biggest challenge since the automotive environment is extremely sensitive to component cost.
- Power density: Modules must be optimized for mechanical integration into highly compact inverters that are mounted in space-restricted engine compartments.
- Reliability: Today’s standard industrial interconnect technologies might turn out to be a serious bottleneck to achieve automotive performance requirements. This results from harsh environmental conditions (ambient temperatures, severe vibrations, humidity), strong cyclic loads and from future trends towards miniaturization and inverter integration to the electric motor.
Power module design
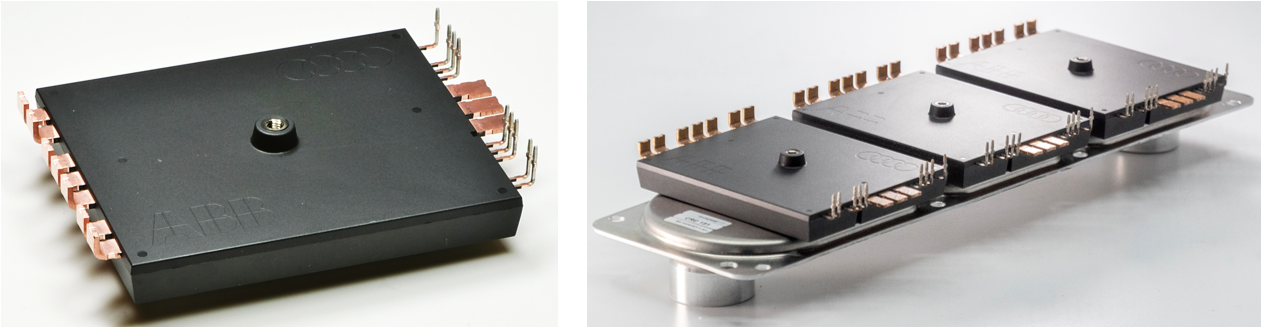
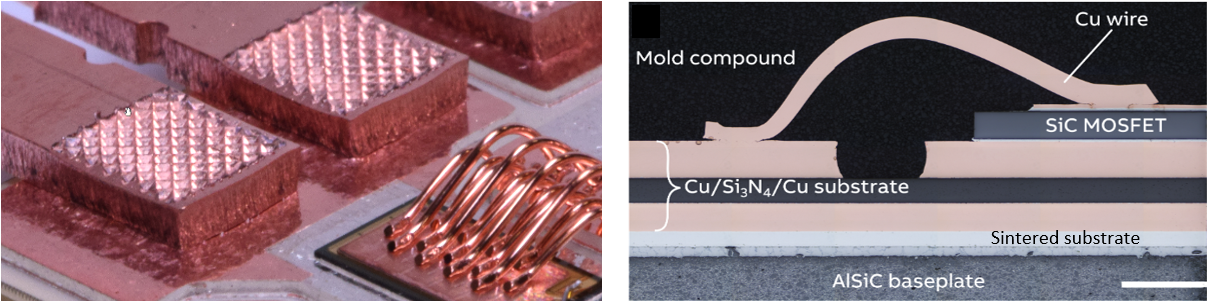
A SiC/ Si power module platform is developed to address these automotive performance requirements. The design approach is characterized by the following features (Fig. 2 and 3):
- Mold modules: A mold module approach is selected that does not require any housing (cost benefit) and that provides excellent environmental protection, cycle reliability and protection against shock, vibration and handling damage.
- Solderless interconnections: A completely solder-free power module is realized for the highest cycle reliability and robustness standards. All interconnections are either sintered or welded. In addition, the device topsides are bonded by copper wire.
- Minimized parasitic inductances: To allow for SiC fast switching, power loop and gate loop inductances as well as coupling coefficients are rigorously minimized (commutation loop inductance: 6.2 nH)
- Screwless cooler integration: A low-cost cooler enclosure is realized by laser welding of mold modules into a cooler structure based on cheap embossed aluminum sheets. In this manner, a compact three-phase inverter module is achieved without the need for screwing or clamping of O-ring sealings that could pose a risk of leakage.
- Scalability: The module offers several aspects of scaling. Two different substrates are applied to assemble either a high-power SiC, or a lower-power Si version for the identical external outline. In addition, the module cost can be scaled by applying different power module component materials (substrates, baseplates, bond materials) to optimize for the right cost-performance ratio for the specific target vehicle.
Validated performance
Double-pulse switching and accelerated stress tests of passive thermal cycling, shock cycling, active power cycling, as well as high-temperature and high-humidity storage tests are conducted to validate the power module performance. In summary, the following results are achieved:
- Successful switching in 2-pulse test, total switching losses as low as 12 mJ at 400 A, 800V
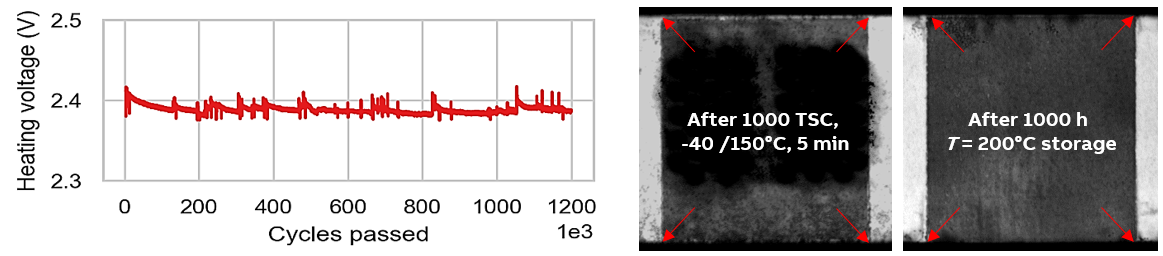
- Power cycling capability of > 1.2 million cycles at T = 100 K, Tjmax = 200 °C (Fig. 4 left)
- No significant aging upon 1000 temperature cycles -40/+150 °C (Fig. 4 center)
- Test modules passing 1000 h of HTRB 200 °C and 1000 h H3TRB at 960 (Fig. 4 right)
We conclude that an automotive SiC and Si power module platform is available that targets inverter classes of passenger and commercial EVs in the power range of 150 – 350 kW. High-reliability packaging technologies are employed enabling operation up to Tj = 200 °C.
References
[1] J. Schuderer, C. Liu, N. Pavlicek, G. Salvatore, JY. Loisy, A. Schröder, D. Torresin, T. Gradinger, D. Baumann, F. Mohn, A. Apelsmeier, “High-Power SiC and Si Module Platform for Automotive Traction Inverter”, PCIM Europe 2019.
[2] International Energy Agency, “Global EV Outlook 2018”, 2018, available online.