YUMI® EXTENDS ITS HELPING HANDS TO HOSPITALS AND LABS
Robots are no longer limited to manufacturing environments and dirty workshops. Increasingly, they are becoming a key part of laboratories, supporting everything from R&D in the pharmaceutical industry and universities to healthcare testing in medical facilities. An example is ABB’s YuMi® collaborative robot, which has already established itself a niche performing a range of repetitive, delicate, and time-consuming laboratory activities, such as dosing, mixing, and pipetting, sterile instrument kitting and centrifuge loading and unloading.
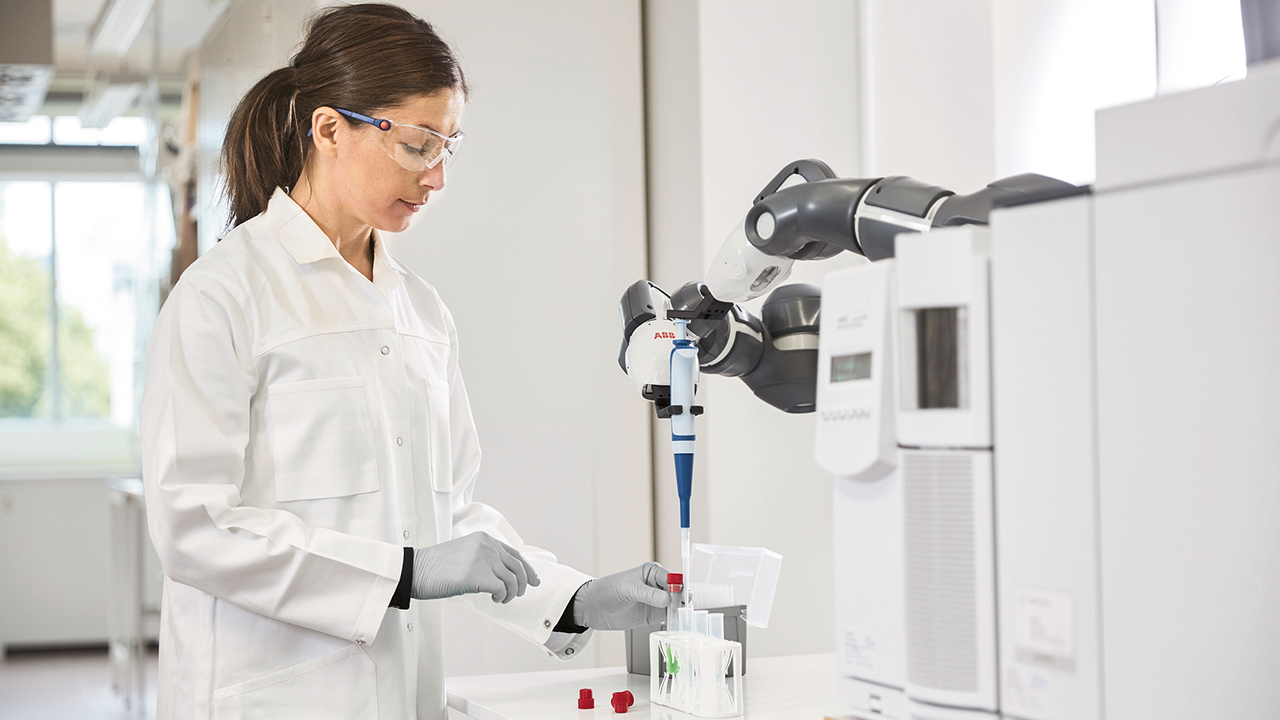

YuMi® is unique on the market due to its inherently safe design. With rounded, padded arms, collision-detection, and no pinch points, it is able to operate safely among its human colleagues in relatively unstructured environments with no need for added safety measures, such as fencing. This enables it to take on a range of repetitive, high-volume tasks, even when they require human-like dexterity or might change at short notice. For example, YuMi® can support process tasks such as device tending, collection and storage, sample transportation and filing alongside human lab workers.
In October 2019, ABB opened a research center at the Texas Medical Center (TMC) in Houston to investigate new robotic and automation concepts for medical facilities and laboratories. Prototype technologies showcased by ABB at the center include YuMi® robots that may be able to aid in centrifuge tending and test tube handling systems and an IRB 1200 robot designed to automate liquid transfers in a pipetting application.
Another prototype concept under development is a mobile dual-arm YuMi® robot. Designed to assist staff with laboratory and logistics tasks in hospitals, it may be able to sense and navigate its way around its human co-workers autonomously, while learning to find different routes from one location to another.
NEW SOLUTION SIMPLIFIES MACHINE-ROBOT INTEGRATION
Thanks to a melding of resources between ABB and B&R1, machine builders will soon be able to offer their products with an integrated robot. Furthermore, their machines will be easier to operate as there will be only one user interface for machine and robot.
The solution allows machines on the factory floor to communicate with integrated robots in real time. In a nutshell, the solution optimizes communication between B&R servo drives and the motors in ABB’s robots.

A practical example of what has been achieved to date is the detection of an imperfection by a B&R vision camera. Here, in less than a millisecond, the data is converted into a control command for an associated ABB robot, and the defective workpiece is removed from a production line without any manual intervention and without affecting the speed of the manufacturing process. Since the machine application automatically calculates optimized motion profiles, it significantly reduces overall processing time while improving productivity.
Behind the solution, which integrates ABB robots into the B&R control system, is a single architecture that melds the information needed by these two previously separate systems. This eliminates the need for a dedicated robotics controller, a separate control cabinet and specialized personnel for specific robotics languages.
Integration is supported through the use of pre-configured software modules that make robotics applications easy for machine builders to create. B&R’s modular preprogrammed software (mapps) allows users to implement complex and highly dynamic applications without having to write new code, thus dramatically reducing development times. All in all, ABB’s new machine-robot integration solution adds up to an unprecedented level of precision when it comes to the coordination of machine processes with robots.
Footnote
1) B&R is an automation and process control company that joined the ABB Group in 2017.
SAVING ENERGY WITH IE5 SynRM MOTORS
The traditional induction motor (IM) has inherent drawbacks that arise from its asynchronous speed – such as rotor heating losses, which decrease efficiency and component and bearing lifetime. Since IMs use around one-third of the world’s electricity, there is a clear need for a more efficient product. Enter, the IE5 synchronous reluctance motor (SynRM), which is characterized by its high energy efficiency and reliability, and low maintenance needs.
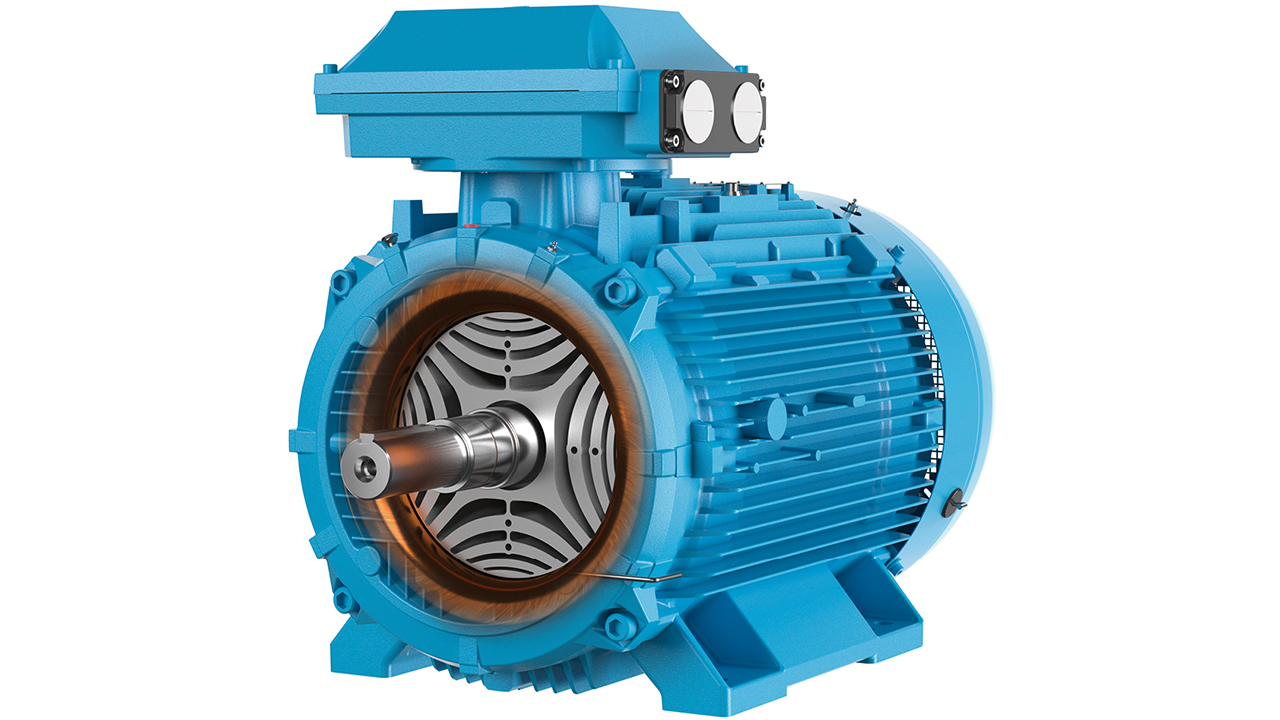
SynRMs work on a very elegant principle that is practicable only since the advent of sophisticated variable-speed drive (VSD) control electronics. In SynRMs, the rotor is designed to produce the smallest possible magnetic reluctance (resistance to magnetic field flow) in one direction and the highest in the direction perpendicular. The rotor turns with the same frequency as the VSD-rotated stator field.
With neither magnets nor cage, rotor construction is more reliable than an IM’s, which lessens maintenance needs. The SynRM’s lower operating temperature delivers longer insulation and bearing lifetimes and lengthier bearing greasing intervals. Adding an ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor provides remote condition monitoring capability.
SynRMs provide a higher power density than an IM and perform better, even at partial load. With a low-inertia rotor, SynRM response is fast, and torque and speed control accurate. The SynRM hardware is plug-in compatible with ABB’s equivalent IMs, making upgrade easy.
The potential of SynRM technology has not been fully explored and higher efficiency levels are quite feasible.
DIELECTRIC TESTING IN A VIRTUAL HIGH-VOLTAGE LAB
Dielectric dimensioning is a crucial aspect of medium- and high-voltage devices like switchgear and transformers. When introducing a new device, manufacturers must certify the product against dielectric type tests defined by technical standards. The prediction of test results is typically supported by electrostatic field computations that are compared with the critical values specified for the given materials, such as gases, liquids and solids – and interfaces between them. However, this approach is often insufficient because dielectric failures do not have a simple relation to field strengths.
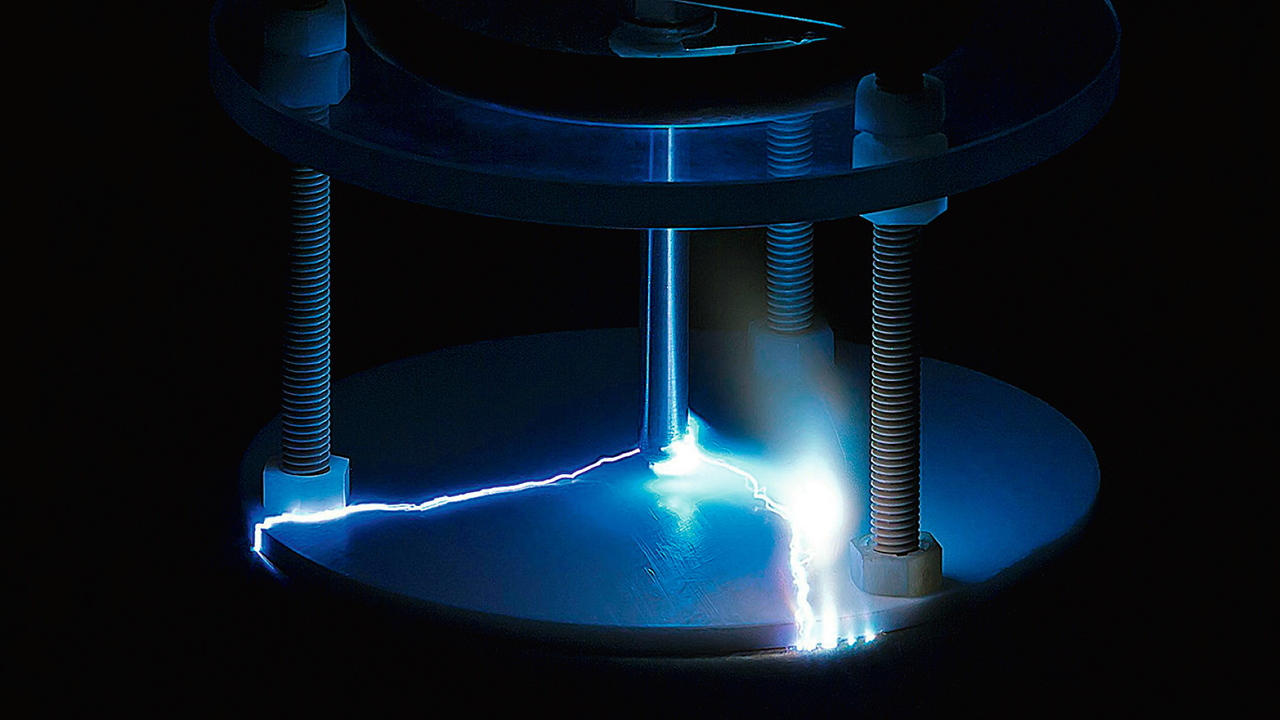
The ABB simulation tool, Virtual High-voltage Lab (VHVLab), provides a software framework focused on the prediction of dielectric test results and is aimed at closing the gap between numerical computations and experiments. VHVLab’s predictions are achieved by combining engineering simulations with empirical knowledge obtained from experiments and first-principle simulations of microscopic models. This type of software is not available commercially because the simulation procedures integrated into VHVLab are derived from ABB test experience gained in a real high-voltage laboratory. Such a tailored platform is a competitive differentiator to commercial simulation software and allows for faster design loops. The development of VHVLab has been driven by industrial research supported by specialized academic partners such as SINTEF – an independent research organization in Trondheim, Norway – who built an experimental setup that enables a flexible choice of experimental configurations.
The tool offers a collection of numerical procedures and empirical rules that allow engineers to evaluate, visualize and understand discharge phenomena. In this context, VHVLab is not only an engineering tool but also a knowledge database into which the experience of researchers and developers has been gathered, providing a foundation for future digital testing.
PLUGGING INTO FAST EV CHARGING
Cities are under pressure to provide cleaner, quieter transportation solutions. With this in mind, ABB has introduced the Terra 184, the most compact high-power charger with the highest power density on the market. The latest member of ABB’s best-selling Terra family of chargers, the Terra 184 is fast, compact, robust and provides the ability to charge up to three vehicles simultaneously, thus maximizing convenience for drivers and revenue for charging operators. With a charging power of 180 kW, the new charger is ideal for roadside parking and charging, as well as for fast charging terminal installations for e-taxi and other (electric) fleets.
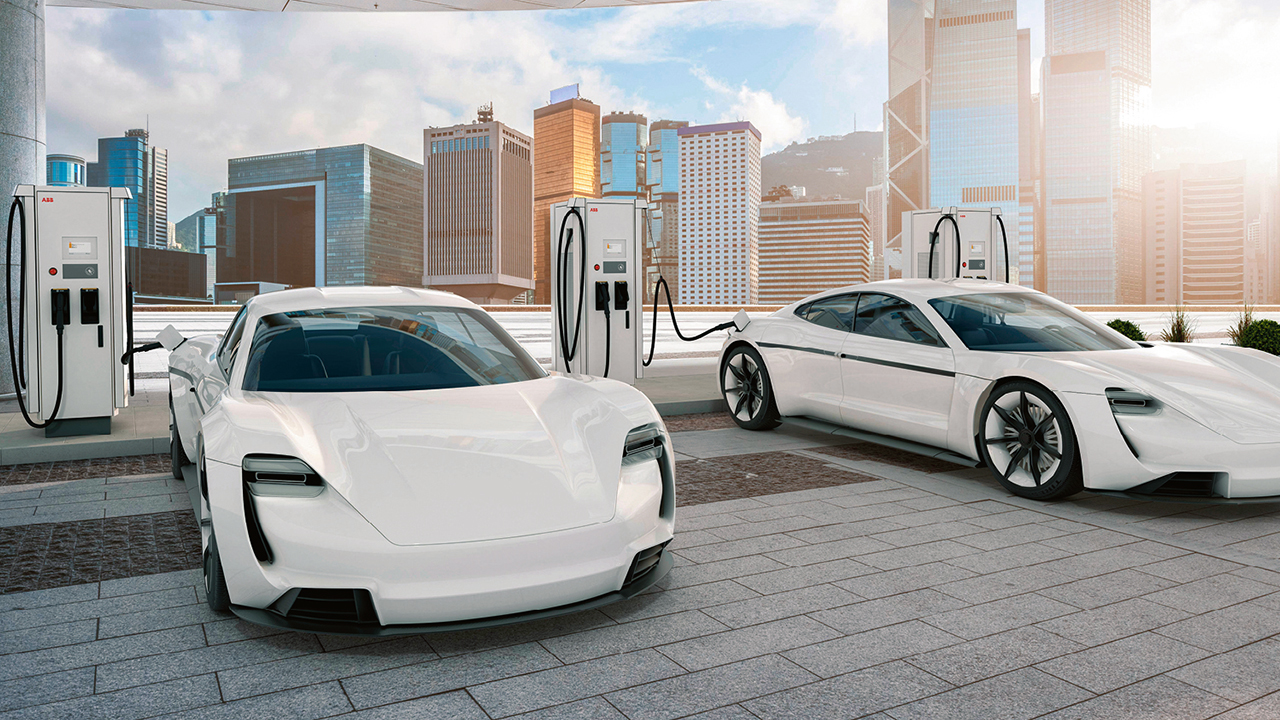

The Terra 184 can be used by vehicles of all sizes, be it the newest existing vehicles or planned cars, buses and trucks. But unlike other high-power chargers, it comes with a footprint of less than 0.5 m2, the same as the current Terra 54 model. Indeed, its innovative design means there is no need for separately installed power cabinets, thus offering an ideal rapid and compact solution for cities with limited space.
The Terra 184 supports all the charging standards on the market, including CCS, CHAdeMO and AC, and caters to the needs of all batteries up to 920 V. It is highly customizable, with features including customized credit card payment terminal, screen and cables.
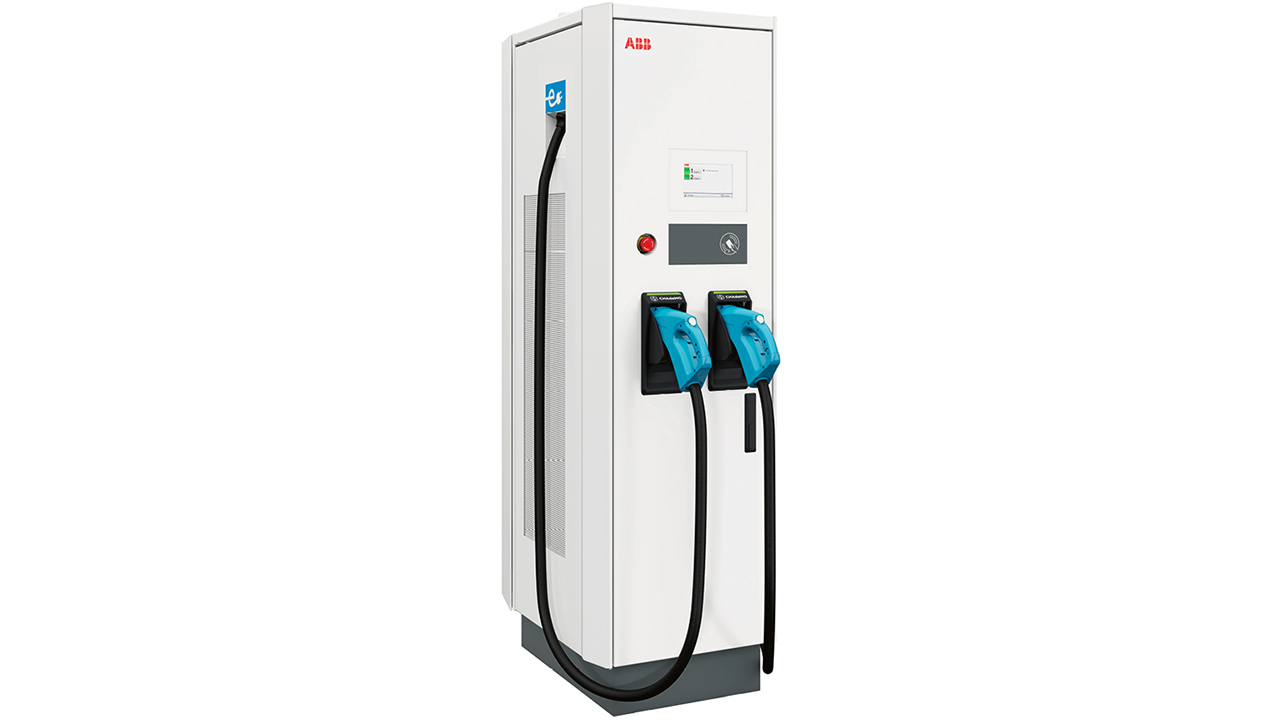

For added flexibility, operators of other Terra models, such as the Terra 94 and 124, will be able to upgrade their charging solution to the Terra 184 by simply adding power modules.
Since entering the EV-charging market a decade ago, ABB has sold more than 14,000 of its DC fast chargers. ABB recently received the Global E-mobility Leader 2019 award for its role in supporting the international adoption of sustainable transport solutions.
REALIZING CLOSED LOOP CONTROL OF STEEL FLUID FLOW IN SLAB CASTING MOLDS
Steel production requires both high productivity and quality end-products and this depends on fluid control during slab casting. Flow Control (FC) Mold G3 employs both DC and AC magnetic fields in the slab continuous caster mold to control the flow speed of liquid steel. ABB’s Optimold Control solution is the only industrial solution to offer online flow speed measurement and the feedback signals necessary to realize automated control of the FC Mold G3. Recently developed, ABB Ability™ Optimold Monitor is a system in which high resolution optical fibers are installed in the copper plate to measure temperature distribution; this is converted into a flow speed signal using an algorithm developed at ABB. The high resolution and immunity of this technology to electromagnetic disturbances is advantageous.
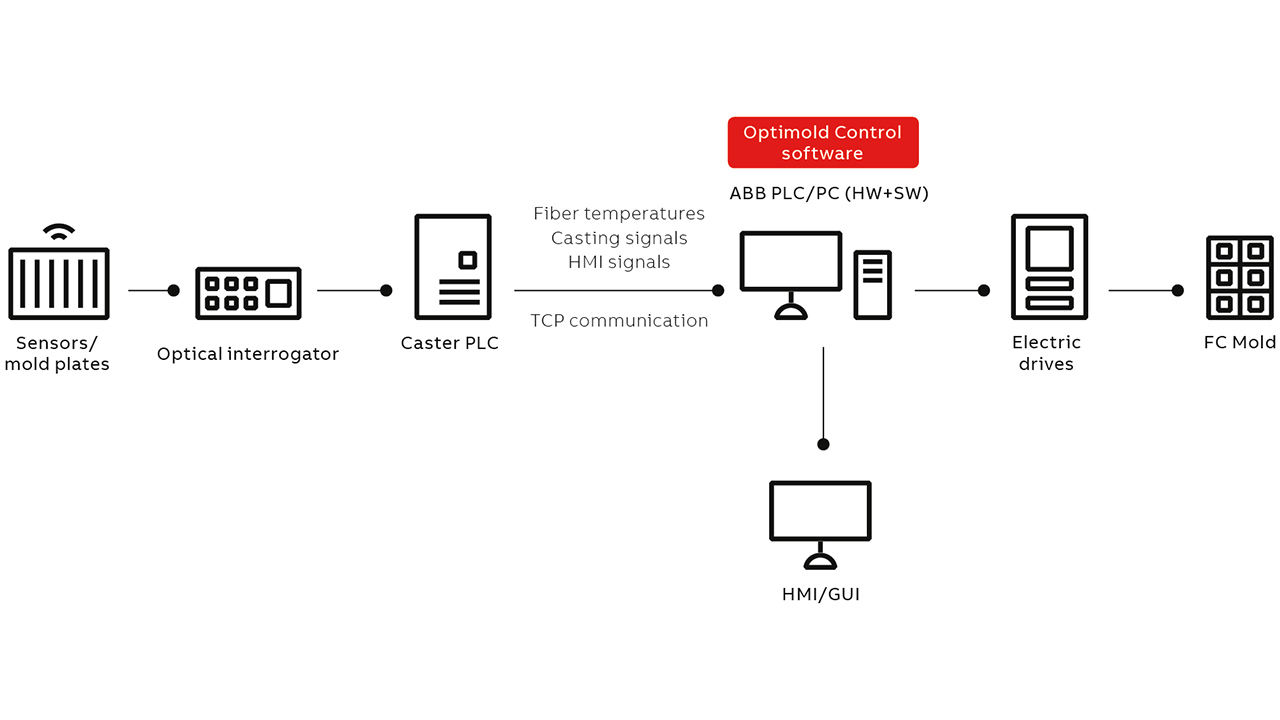
In September 2019, ABB established a world record at Hyundai Steel in Korea; the installation involved almost 5,000 measuring points – a huge advantage over traditional methods using thermocouples in which only around 100 points can be measured. ABB Ability™ Optimold Control is a software package that connects ABB Ability™ Optimold Monitor and FC Mold G3 to deliver closed loop control of the FC Mold G3. At this stage, the ABB Ability™ Optimold Control will be added to the deterministic control software already included in every FC Mold installation. Process defects caused by SEN clogging and unstable argon gas are counteracted with the real time control algorithm through adjustments of a predetermined magnetic field.
The first ABB Ability™ Optimold Control installation is planned for Hyundai Steel in 2021 and, in the future, it will be further developed into an autonomous system supported by artificial intelligence. ABB Ability™ Optimold Control system will allow steel manufacturers to quickly identify and correct variations in the casting process that might negatively impact safety, energy efficiency and product quality, thus ensuring optimal casting.
THE DIGITAL LIGHTHOUSE PROGRAM: IGNITING TRANSFORMATION
In 2017, to catalyze digital innovation, ABB launched the digital Lighthouse Program, which selected and partially financed the development of innovative digital solutions in collaboration with customers. ABB believed the Lighthouse Program could marry good internal ideas with the necessary funding, resources and customer co-innovation to shorten time to market.
The primary goals of the program were:
• Accelerate the development and deployment of innovative digital solutions built on the ABB Ability™ Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platform.
• Encourage co-development of solutions with customers, engaging them at an early stage.
• Speed up ABB’s adoption of leading-edge digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality, virtual reality, digital twins and blockchain.

Applicants with good ideas identified customers willing to co-develop new digital products, explained what customer pain points the product would address, outlined the obstacles to success and how the program’s support would overcome them, and highlighted the immediate and long-term revenue potential.
Two and half years later, at the program’s completion, 66 minimum viable products (MVPs) had been deployed with customers and over 40 customer testimonials published. To date, 30 products developed under the Lighthouse Program have been released commercially. But the most important feature of the program is the culture of digital innovation fostered within ABB, which means that, in future, far fewer digital innovations will now sit untried and untested on the shelves.
ABB BRINGS ETHERNET-APL TO HAZARDOUS AREAS
Since 2011, ABB has been working within a consortium of process automation industrial partners, backed by industry standard development organizations, to drive the standardization of Ethernet-Advanced Physical Layer (APL). Ethernet-APL extends Ethernet by combining the simplicity of 4 – 20 mA wiring with a swifter Ethernet-type of bandwidth and protocol support; and yet is simple and robust enough for use in Hazloc areas. With their domain expertise in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices, ABB is able to leverage the benefits of Ethernet, such as the multi-protocol capability, to provide connectivity with broadly distributed two-wire, loop-powered field instruments for use in potentially hazardous environments.

ABB’s research has focused on OPC UA technology, a new universally applicable communication protocol that provides heightened levels of cyber security, semantics and information models that obviate the need for descriptions. By making OPC UA technology usable for small resource-constrained field devices, ABB is dissolving the border between Operation Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT).
Successful tests of ABB’s OPC UA solutions for a flowmeter, conducted in 2017, and level and pressure transmitters equipped with APL evaluations boards, conducted in 2019, demonstrated just how well Ethernet-APL and OPC UA integrate with modern process plant architectures as defined by standardization organizations, eg, NAMUR Open Architecture (NOA), Module Type Packages (MTP) or Open Group, O-PAS (Open Process Automation System).
With the expected 2021 release of Ethernet-APL standard with the underlying IEEE802.3cg (10BASE T1L) standard, the IEC standard 2-wire intrinsically safe Ethernet (2WISE) for Ex-protection and the release of definitions for Ethernet-APL implementation, the adoption of field-level communication supported with Ethernet communication protocols, eg, OPC UA, among others, is just around the corner. The targeted launch of Ethernet-APL in June at the ACHEMA 2021 trade show will be accompanied by ABB and other automation suppliers who will introduce the first Ethernet-APL products, thereby initiating a new phase of safe, secure and practical field-level communication for process plants.
SMART SENSOR-BASED INFORMATION ECOSYSTEM
Mechanical components such as bearings and gear reducers are generally located in hard-to-access locations, thus making their inspection difficult and time consuming. The ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor for mechanical products provides a solution. Designed to reduce downtime, improve reliability, and operate safely, this wireless sensor provides an easy-to-use solution for monitoring the health of Dodge mounted bearings and gear reducers. The sensor indicates abnormal vibration- and temperature-related conditions, thus allowing users to avoid down time by planning maintenance before problems occur.
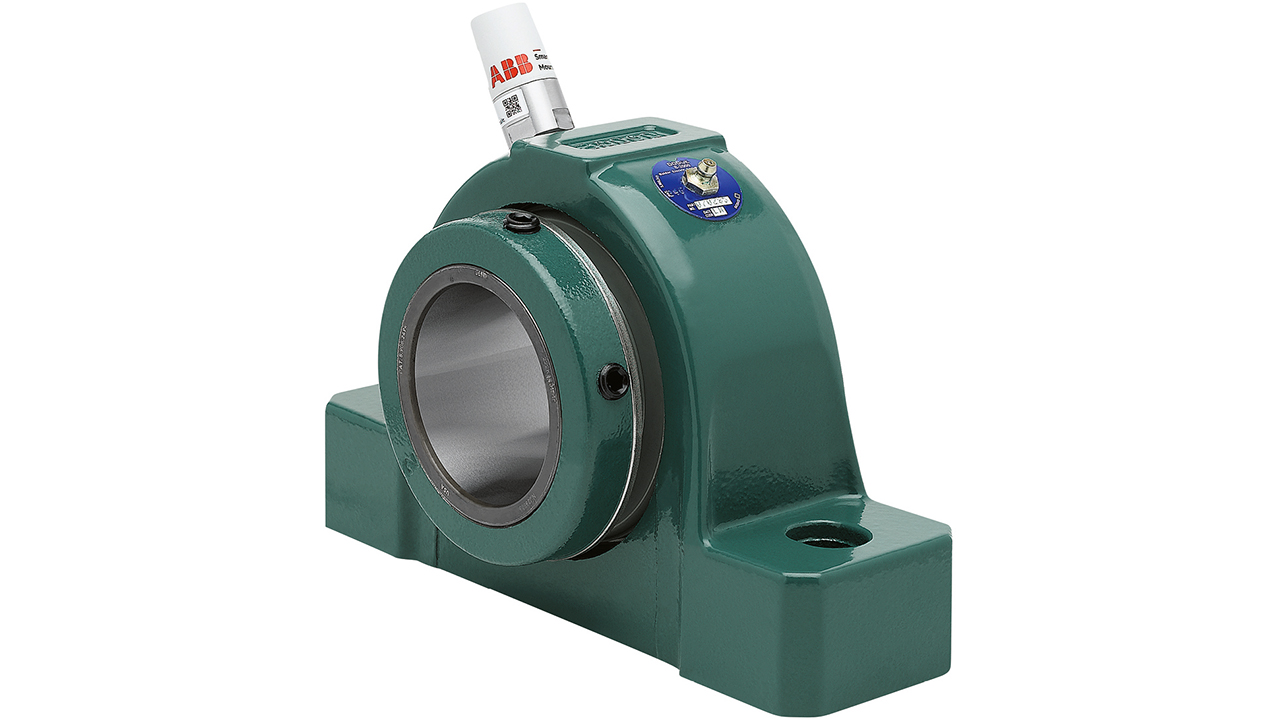

Now, thanks to new firmware, the Smart Sensor can be updated to also display features such as velocity RMS, change measurement interval, change accelerometer range, and start/stop detection. These features, all of which are the result of customer feedback, significantly enhance the Smart Sensor’s existing capabilities.
The Smart Sensor provides users with complimentary access to the ABB Ability™ digital platform, and thus to the power of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Data from multiple sensors can be transmitted by a user’s smartphone or ABB’s new Plug & Play gateway to a secure, cloud-based server, where it can be analyzed by advanced algorithms to identify bearing faults. The data is stored in the ABB Ability™ digital platform, from which it can be accessed and graphically displayed for further analysis.
This new plug & play solution, which relies on two of the most popular cellular providers in the U.S., provides seamless connectivity and data analytics from sensors and cellular networks all the way to the ABB Ability™ digital portal.
GAS LEAK DETECTION COMES OF AGE
Almost 3 million miles of pipeline infrastructure crisscross the United States, delivering 25 trillion cubic feet (or 700 billion m3) of natural gas to 75 million customers1. With half of this pipeline infrastructure built before 1970, it can be prone to leaks. Gas lost through leaks leads to increased costs to consumers, supply and maintenance disruptions, as well as serious safety and environmental issues.
A 2018 study published in Science2 found that the volume of natural gas leaking from across the supply chain would be enough to fuel 10 million homes, and is worth an estimated $2 billion per year. Further, pipeline leaks are a contributor to climate change and are negating some of the environmental benefits of switching from coal to natural gas. Methane, the main constituent of natural gas, is a greenhouse gas 21 times more potent than carbon dioxide.
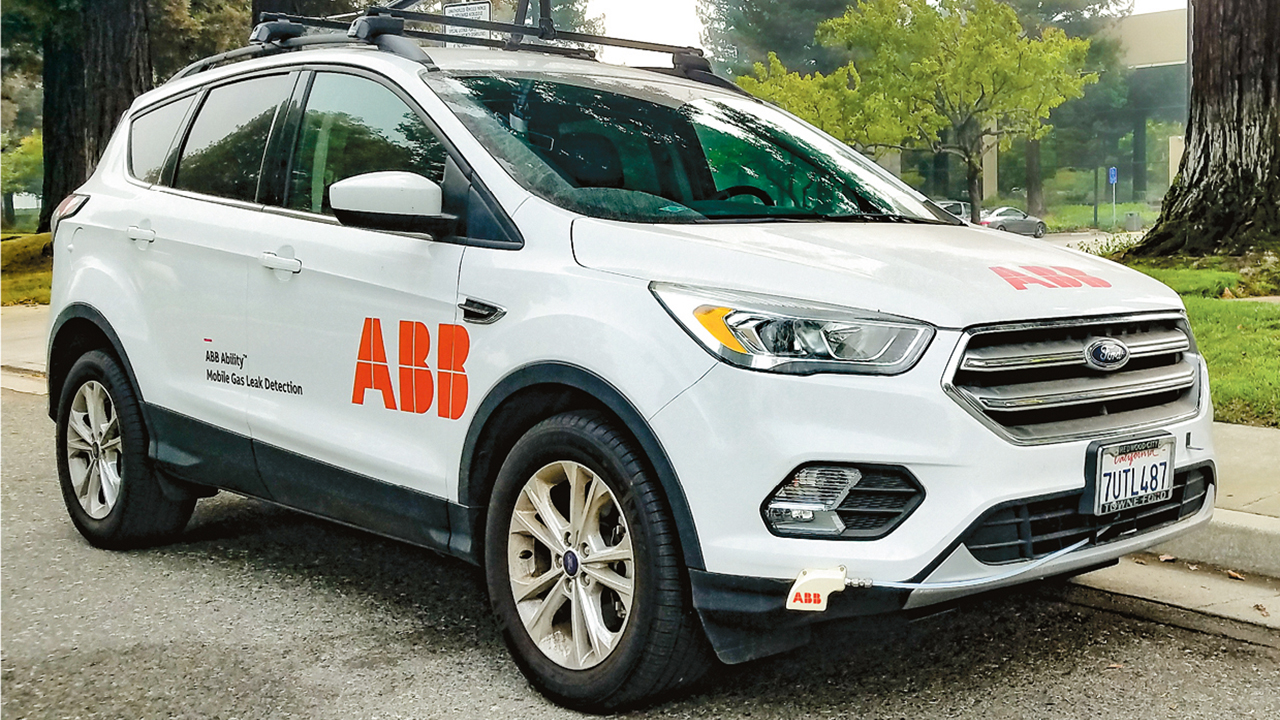

The first step to fixing gas leaks is finding them. For years, traditional leak detection has been ground-based with hand-held detectors that are slow and labor-intensive. Such methods do not meet the demands of the 21st century digital economy for fast, accurate, and transparent data.
The ABB mobile solution is a highly-sensitive vehicle-based system that measures and reports minute concentrations of methane in the air, along with wind speed and direction, permitting leakages to be pinpointed remotely. The detection system features ABB’s patented methane/ ethane analyzer, a GPS, a wind speed anemometer, and proprietary leak detection software. Electronic compliance records are generated on a map and can be accessed on a mobile device by a service team or in the operations center. This vehicle-based solution can survey a 10 to 25 times greater area per hour compared to traditional methods. •
Footnotes
1) “Natural gas explained, Natural gas pipelines”, EIA, https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/index.php?page=natural_gas_pipelines
2) R. A. Alvarez et al.*, “Assessment of methane emissions from the U.S. oil and gas supply chain, Science, https://science.sciencemag.org/content/361/6398/186?rss=1
ABB’S NEW GENERATION OF SMALL ROBOTS FOR GREATER FLEXIBILITY AND PERFORMANCE
Evolving customer tastes and skill shortages have led manufacturers to develop highly customized and thus small production batches – this low-volume high-mix production philosophy requires greater performance, flexibility and compactness. ABB’s new generation of small robots are key in meeting these objectives. Relying on a modularity platform to develop customized robots faster than ever before, ABB’s IRB 910INV, IRB 1100 and IRB 1300 robots represent this new generation of small robots. Developed in one-third the time of conventional methods, these robots are available in seven primary variants, and over twenty-two configurations.
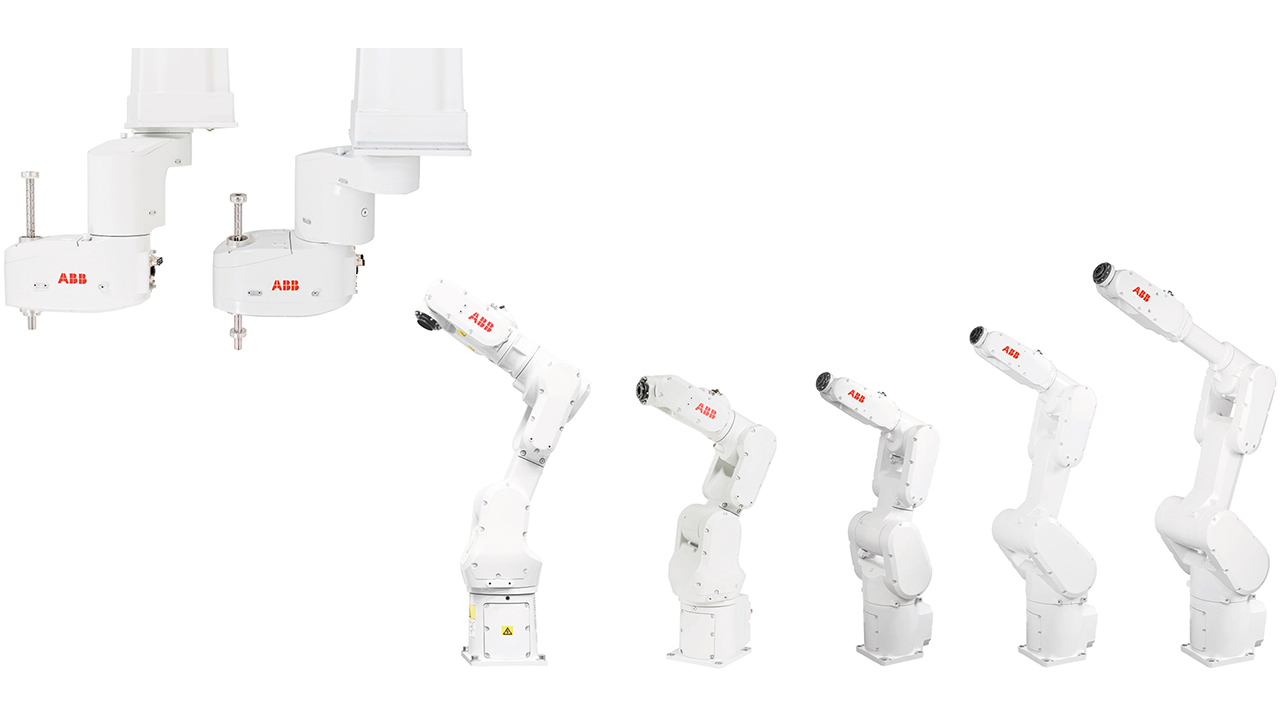

Designed with reach, payload, and accuracy to reflect customer and application needs, eg, loading, assembly, and treatment processing, these robots serve the automotive, electronics, semiconductor, healthcare, and food and beverage industries in harsh and complex factory environments, where ingress protection, ISO clean rooms, or food grade lubrication is required.
Highly flexible and space saving, the IRB 910INV SCARA robot has a clean room option. Available in two variants: with a 350 mm reach and payload up to 3 kg or with a 550 mm reach and up to a 6 kg payload, this robot is ideal for the electronics industry. IRB 1100 standard comes with IP40 protection and a more rugged IRB 1100 option with IP67; both are available in two variants: 475 mm or 580 mm reach, achieving best-in-class payload and repeatability (0.01 mm).
This robot provides 35 percent increased productivity and saves 10 percent space for high quality manufacturing. Recently launched, IRB 1300, with standard IP40 protection comes in three variants: with a reach of 900 mm, 1,150 mm and 1,400 mm and repeatability between 0.02 mm to 0.03 mm.
All variants offer the option of absolute accuracy to enhance accuracy performance for high-precision demanding applications. Thus, ABB’s new generation of modularized small robots provide the customization, flexibility and compactness that diverse manufacturing industries require
DRIVE CONNECTIVITY PANEL
All across industry, users of ABB variable-speed drives have been looking for a plug-and-play way to combine internet connectivity, data collection, cloud analytics and visualization. Now, with ABB’s pioneering Drive Connectivity Panel, they need look no longer. Just minutes after installing the Connectivity Panel, data can be analyzed in the cloud portal.

The Drive Connectivity Panel collects the drive’s operational data and sends it directly to the cloud via a cellular network, using narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT). The Drive Connectivity Panel is the only product on the market that enables cloud connection without occupying a data collection I/O port. Data transfer is also kept safe as it is encrypted within the panel and uploaded via the secure NB-IoT cellular network – dedicated to industrial devices – to the ABB Ability™ cloud platform.
The availability of the latest mobile technology means that when the panel is located in an area with normal signal coverage, it can interact with the cloud services – even if the drive is installed in the basement.

The NB-IoT solution is ideal for condition monitoring in applications requiring a basic level of equipment analytics and alarm notifications but that use low data volumes. Continuous data uploads allow remote health monitoring of ABB drives, event notifications, operational KPI generation and parameter trend creation. Drive health and performance are visualized in an easy-to-interpret way. The panel’s Bluetooth interface enables an on-demand remote assistance service – ABB Ability™ Mobile Connect for drives – via the Drivetune mobile app.
The Drive Connectivity Panel-based condition monitoring solution is available for purchase in China and is being piloted in Europe and the United States.
THE SYMPHONY OF DATA VALUE CHAINS
The foundational philosophy driving the conceptualization and vision of ABB’s digital offerings is the pursuit of combining scattered bytes of digital noise into synchronized enterprise-wide ecosystems of insights – with an impact that extends across every aspect of operational excellence.
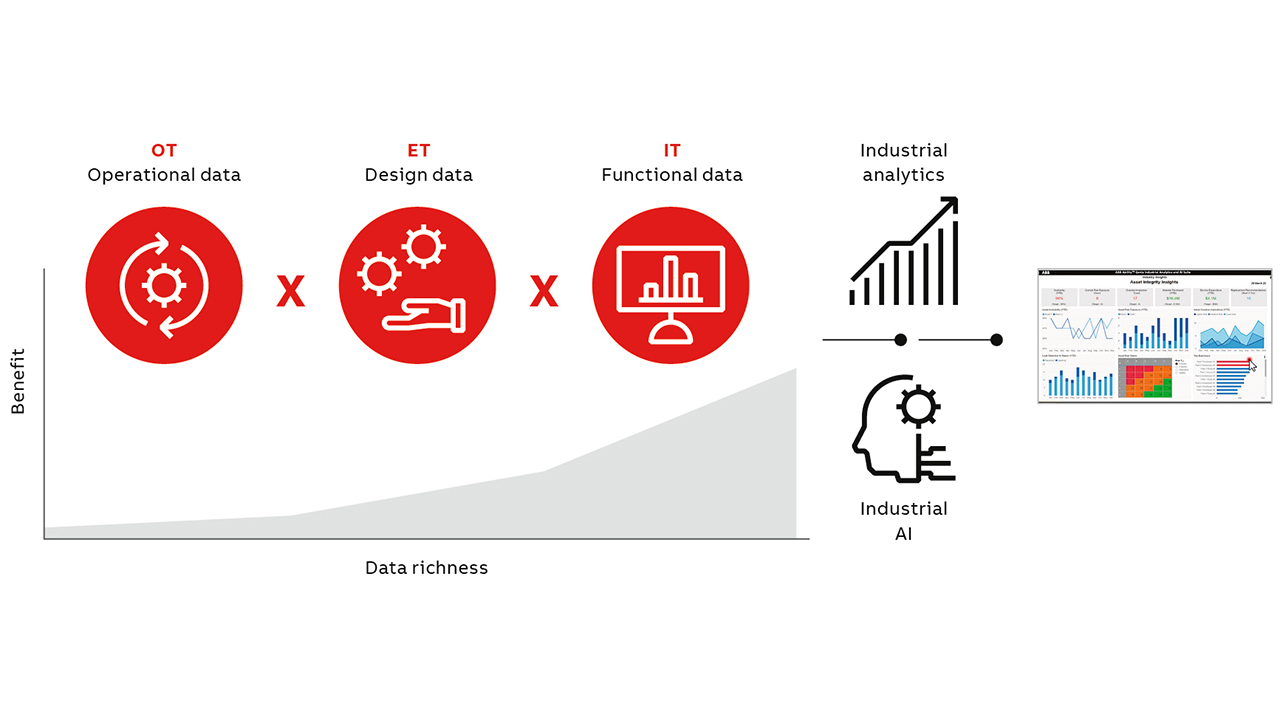
In this context, what ABB Ability™ Genix, the industrial analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) suite, and ABB Ability™ Edgenius, the operations data management tool, achieve together is what is best described as exponential impact; or what ABB calls the X factor. At the heart of this X factor, enabling it, is data aggregation and contextualization: Data from diverse sources, ie, real-time operational data (OT), functional data from IT systems and design data from engineering systems (ET) is brought together into a cognitive data model for the application of industrial analytics and AI or machine learning (ML) driven models.
Typically, data rests in silos with more than 70 percent estimated to remain unutilized for analytics purposes. ABB Ability™ Genix and ABB Ability™ Edgenius help convert cross-functional data into powerful insights through this process of using coherent data models and contextualization. For example, a smart maintenance solution for Azipod® propulsion, was recently developed. This predictive maintenance solution identifies potential anomalies and generates an early warning so that maintenance teams can prevent failure using AI-/ML-based models. The engine for anomalous condition detection and early warning is based on the integration of real-time data, eg, winding temperatures, speed, torque, power and both inlet and outlet cooling air temperatures. Pilot implementations have showcased the benefits: an increased lead time, of over one hour, allows operators to address issues before they turn into catastrophic failure. Thus, ABB Ability™ Genix and ABB Ability™ Edgenius work together to orchestrate a symphony of data value chains
